Pharmacokinetic effect of Astragalus membranaceus and Panax notoginseng saponins on arginine absorption and nitric oxide production in healthy subjects
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/ffhd.v13i6.1104Abstract
Background: To the best of our knowledge, there are no clinical trials conducted with Astragalus and ginseng extracts on nitric oxide (NO) levels in humans. Therefore, this study aimed to examine whether the standardized intake of Astragalus membranaceus and Panax notoginseng saponins (APS) could increase NO production by enhancing arginine absorption and reducing levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine (AMDA).
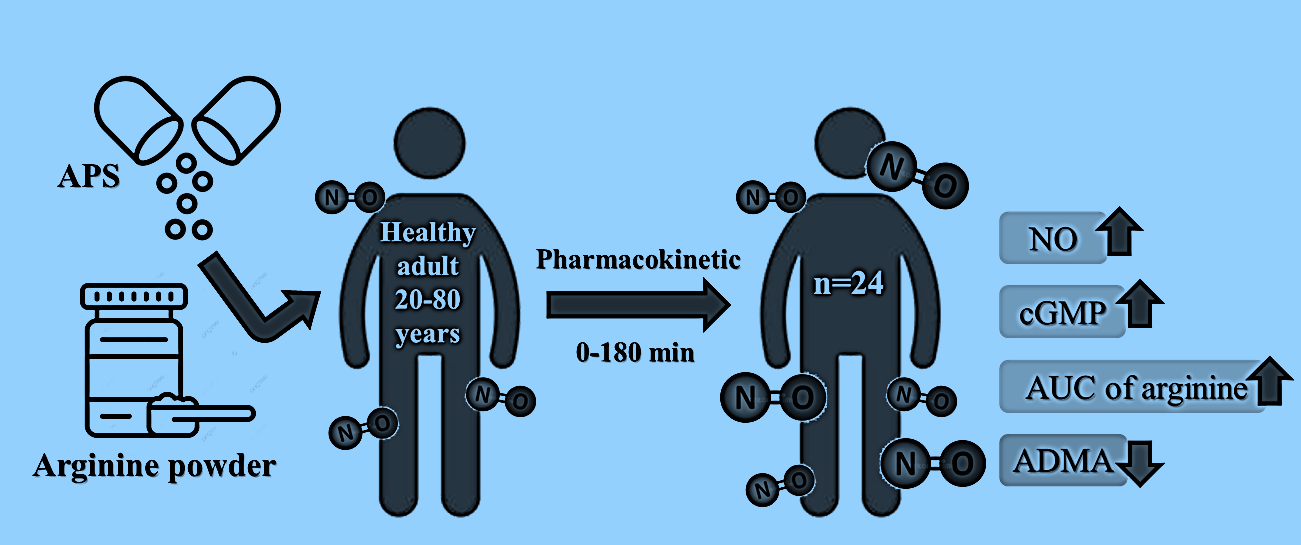
Methods: A clinical trial involving healthy adult participants aged between 20 to 80 years was conducted as a randomized, double-blind, cross-over study. The participants received 5 g of arginine powder and one capsule of APS or placebo twice, with a wash-out period between each administration. Plasma and urine were collected for testing, and 24 subjects were included for analysis after excluding six subjects with great individual differences.
Results:It was found that after APS supplementation, the area under the curve (AUC) of arginine significantly increased by 17.3% (p = 0.041), the maximum concentration (Cmax) increased by 11.1%, and the Arg/ADMA ratio significantly increased by 167.1% (p = 0.007). Moreover, urinary nitrate and cGMP levels increased by 20.8% and 18.9%, respectively.
Conclusions: APS showed increases in arginine absorption, decrease ADMA levels, and enhance NO production. With these findings, the addition of APS to arginine supplements could be advantageous for pre-workout and cardiovascular health.
Keywords:Astragalus membranaceus and Panax notoginseng saponins (APS), arginine, asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), nitric oxide (NO), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)
Clinical trial registration: NCT05024123
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain the copyright of their articles and grant the Functional Food Center (FFC) and its journals the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, including commercial use, provided the original author(s) and source are properly credited. Authors may post and share their published work freely, provided that the original publication in this journal is acknowledged.
By submitting to this journal, authors confirm that their manuscripts are original, not under consideration elsewhere, and that they hold the necessary rights to grant this license. The Functional Food Center encourages open scientific exchange and allows derivative and extended works, provided attribution to the original publication is maintained.