Phytochemistry and nutraceutical properties of Carica papaya (Linn.): A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/dsn.v1i9.991Abstract
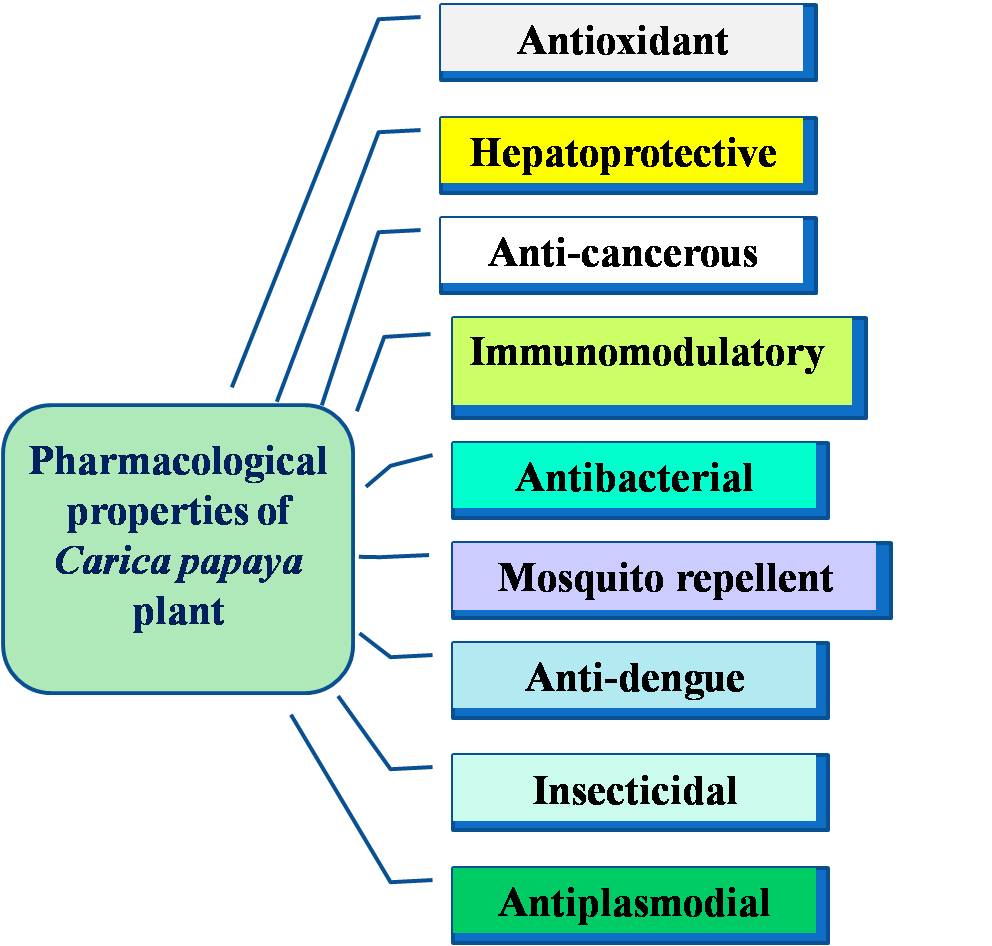
Nutraceuticals derived from a medicinal plant having therapeutic significance are a gift to mankind to acquire healthy life. Carica papaya Linn. (aricaceae) commonly known as papaya. It is a significant fruit tree and is found in tropical and subtropical parts of the world. The extract from various parts of plant especially fruit and leaves contains many phytonutrients viz; vitamin A, B1, and vitamin C, calcium hydrate charcoal, phosphorus, iron, protein as well as some endopeptidases like namely papain, glycyl endopeptidase, chymopapain, and caricain. The extract of this plant is identified to be efficacious against diversified ailments like malaria, inflammation, digestive disorder, Microbes, Fungi, and many infectious disorders. Its prophylactic and therapeutic values enhance immunity and ensure a healthier life. Each part of this plant has its nutraceutical properties.
Keywords: Nutraceuticals, Carica papaya, Papain, Caricain, Chymopapain
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.