Anti-obesity properties and mechanism of action of genistein
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/fffso.v1i7.1111Abstract
Obesity is considered a major health problem worldwide with a constantly increasing incidence, representing a significant public health issue affecting all genders and all ages, even children. The WHO reports alarming information that in 2016, 39% of adults were overweight, 13% were obese, and more than 340 million children and adolescents were overweight or obese. Information from 2020 states that 39 million children under 5 years of age were overweight or obese. With the occurrence of obesity, the risk obesity-related disease incidence, for example, hypertension, stroke, myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, fatty liver, osteoarthritis, obstructive sleep apnoea, dementia, and several types of cancer, greatly increases.
Recent evidence shows the beneficial effects of natural compounds - flavonoids in preventing and treating obesity. Flavonoids, found in various plants, represent active biocompounds that are associated with many beneficial effects on human health, including their noticeable effect in obesity treatment due to their ability to reduce food intake and increase energy expenditure, reduce fat absorption and fat mass, decrease levels of triacylglycerides and cholesterol, and modulate the metabolism of lipids. Our review summarizes the antiobesity effect of genistein, a flavonoid that belongs to isoflavones subgroups. Genistein, a naturally occurring compound, is one of the most known and studied isoflavones that shows many beneficial antiobesity properties. Genistein has the ability to reduce body weight and food intake, increase lipolysis, increase oxidation of fatty acids, decrease adipogenesis, stimulate adipocyte differentiation, and induce adipocyte apoptosis.
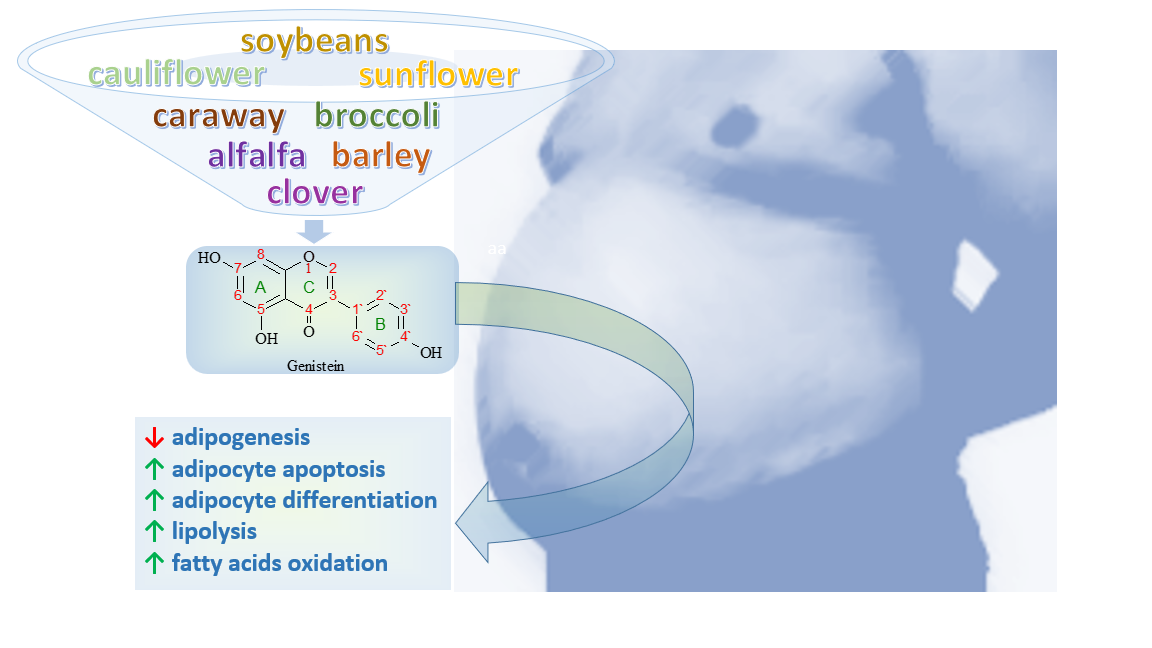
Keywords: Obesity, Flavonoids, Isolavone, Genistein
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.