Evaluation of black seed (Nigella sativa L.) cake and its protein in muffins as a valuable potential functional source for obesity control
##doi.readerDisplayName##:
https://doi.org/10.31989/fffso.v1i6.1107要旨
Background:Due to the use of high-calorie foods and reduced physical activity caused by the modern lifestyle, obesity is on the rise. Obesity occurs by the increase of fat accumulation in the body, causing different complications such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, respiratory disorders, blood pressure, etc., which has become a global problem.
Objectives:The production of functional food that has medicinal properties for controlling or inhibiting diseases is increasingly popular. With the expanding concerns about obesity and its related diseases, it is very important to provide natural controlling or inhibiting compounds. In this study, the functional properties of black seed cake (BSC) and its protein (BSCP) were investigated for obesity control through the inhibition of pancreatic lipase, α-glucosidase, and α-amylase enzymes as well as its antioxidant properties.
Methods:The textural properties and sensory evaluation of muffins, enzyme inhibition properties (inhibiting the effect of enzymes in the obesity process), and antioxidant properties (control or inhibition of side effects caused by body fat oxidation) of BSC and BSCP were investigated.
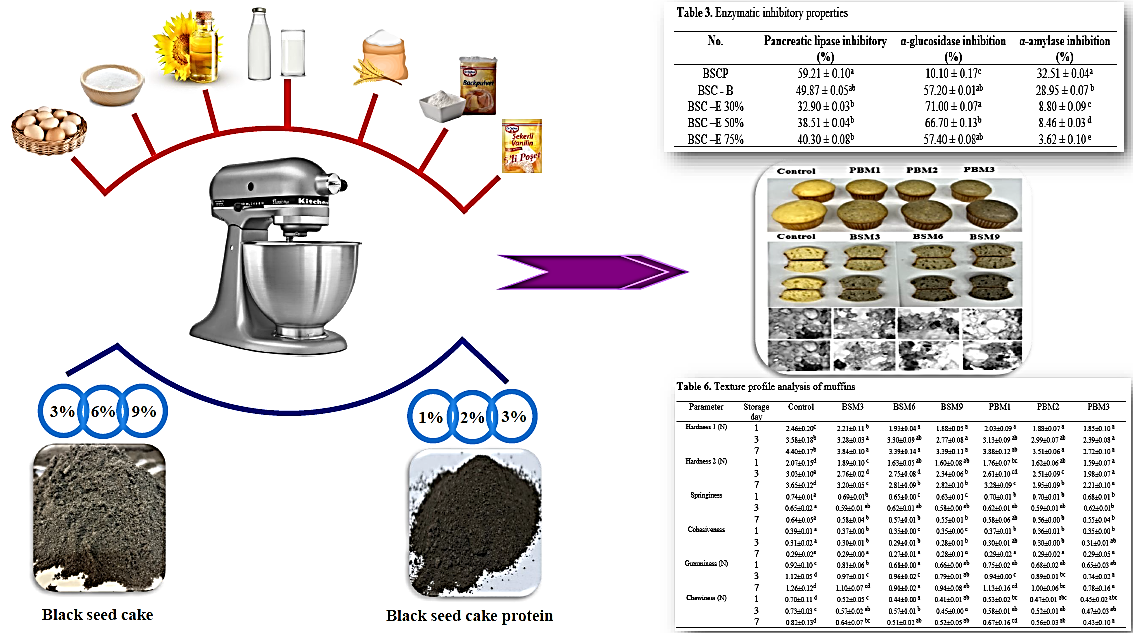
Results:The highest and lowest inhibitory levels of pancreatic lipase are related to black seed (Nigella sativa)cake protein (BSCP) (59.21%) and black seed cake (BSC) (32.90%), respectively. The highest and lowest levels of α-amylase inhibition are related to BSCP (32.51%) and black seed cake in ethanol 75% (BSC-E75%) (3.62%), respectively. The highest and lowest α-glucosidase inhibitory levels are related to BSC-E30% (71%) and BSCP (10.10%), respectively. BSC and BSCP showed high antioxidant activity. The use of BSC and BSCP in the production of muffins (a widely consumed and popular product) to replace flour and oil in the formulation of muffins caused a decrease in L*, b*, but an increase in a*. Hardness, chewiness, springiness, and cohesiveness decreased with the increase of BSC and BSCP content. Samples BSM 3%, BSM 6%, PBM 1%, and PBM 2% were similar to control muffins in sensory evaluation.
Conclusions :From the result of this study, it can be concluded that black seed cake and its protein can be considered a potential efficient source for the production of functional muffins and possibly other functional foods that aim to manage and control obesity, blood glucose, and blood fat. However, more research is needed to fully determine the effectiveness of black seed cake and its protein.
Keywords: Obesity, Black seed cake, Muffins, Diabetes, Blood pressure, Blood fat
発行日
巻号
セクション
ライセンス
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.