Effect Of Curcumin and Luteolin on Drosophila Melanogaster Transgenic Model of Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
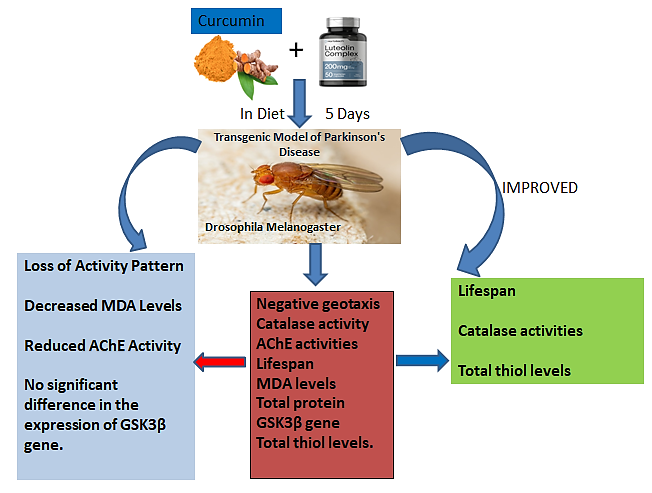
Background:A neurodegenerative disorder called Parkinson's disease is distinguished by Lewy bodies, overexpression of α-synuclein, and dopaminergic neuron loss. Additionally, tremors, bradykinesia, and muscular rigidity are some of the disease's initial symptoms, and they are all linked to the oxidative stress that pro-oxidant reactive oxygen species create.
Objective: This investigation uses Drosophila melanogaster to assess the effects of curcumin and luteolin on a transgenic Parkinson's disease model. The study has substantial clinical value because the results might lead to the creation of cutting-edge treatments for Parkinson's disease.
Methods: Both wild-type and transgenic flies were divided into five groups. The transgenic flies were exposed to normal media, 50 mg/kg of curcumin and luteolin, and 100 mg/kg of curcumin and luteolin treatments, while wild-type flies were exposed to normal media and curcumin and luteolin (100 mg/kg) for five days. To assess the effect of curcumin and luteolin on Drosophila transgenic model of PD, we conducted experimental tests including negative geotaxis assay, catalase activities, AChE activities, fly lifespan, MDA levels, total protein, GSK3β gene expression, and total thiol levels.
Results: The transgenic flies with and without treatment expressed similar expression of the GSK3β gene, as well as a dose-dependent delay in the pattern of activity decrease, increased lifespan, higher catalase activities, increased total thiol levels, decreased MDA levels, and reduced AChE activity.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that the combination of curcumin and luteolin could serve as a supplementary approach in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Parkinson’s Disease, Neurodegenerative, Lewy Bodies, Drosophila Melanogaster, Transgenic, Curcumin, Luteolin.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.