A Review on alternative treatments of gestational diabetes mellitus: Focus on phytotherapy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/ffs.v3i9.1137Abstract
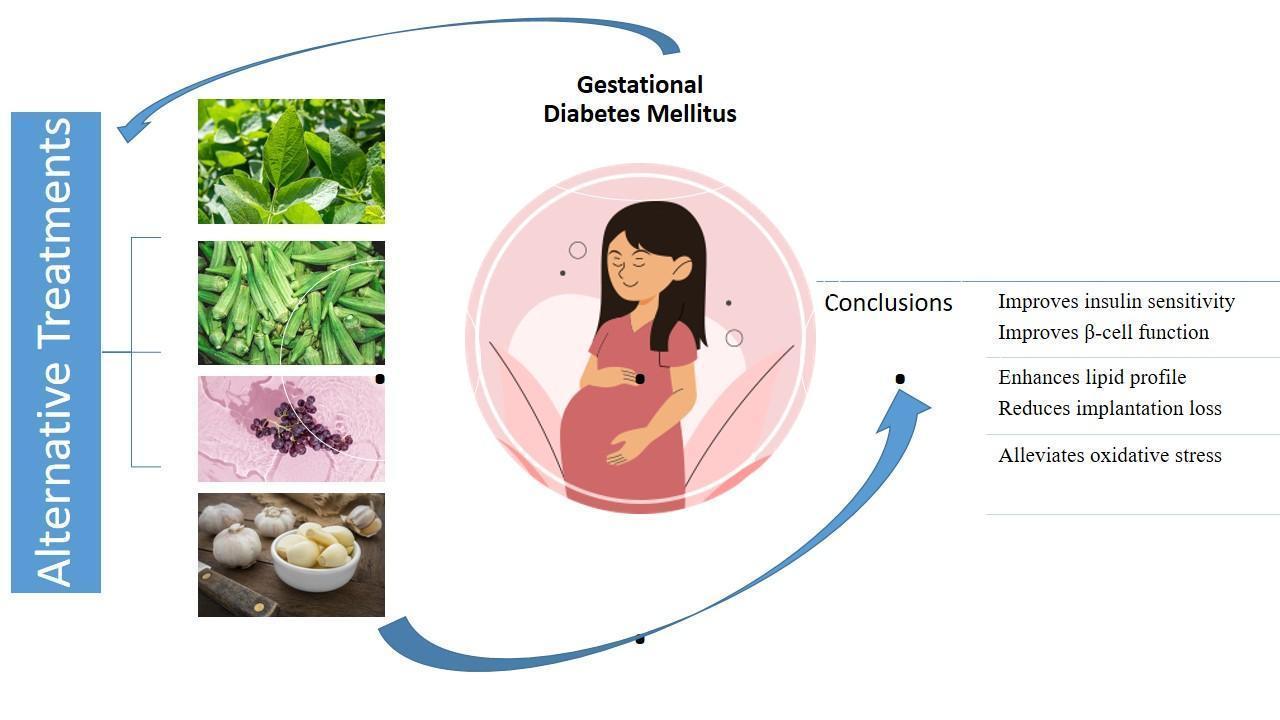
Gestational diabetes (GDM) refers to glucose intolerance which manifests as hyperglycemia during pregnancy. Some features related to GDM include insulin resistance, an abnormal increase in weight and increased risks of complications during delivery. Severe cases of GDM can result in hyperinsulinemia, macrosomia, obesity, and type II diabetes in the offspring. Due to changes in placental hormones including estrogen and progesterone observed in normal pregnancy, there is a decrease in the sensitivity of target organs to insulin resulting in a compensatory production of insulin to maintain glucose homeostasis. However, this inability of the β-cells to effectively handle this high demand for insulin can result in GDM. Exercise and dietary therapies are the major treatments for GDM and if these two are not effective, oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin injections are usually considered. There have been concerns about the safety of these oral hypoglycemic agents hence, alternative therapies including the use of medicinal plants are being considered. This review, therefore, aims to explore the modes of action of some medicinal plants, functional foods and bioactive compounds as alternative treatments for gestational diabetes. Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, PubMed, ResearchGate were searched for relevant articles published between 2010-2023 using the keywords “medicinal plants and gestational diabetes”, “bioactive compounds and gestational diabetes”, “functional foods and gestational diabetes”. From the research articles, some of the mechanisms of action include reduced blood glucose level, improved insulin sensitivity, lipid profile and oxidative status, increased body weight of offspring. However, further scientific evidence is required to validate and re-validate their safety and efficacy.
Keywords: Gestational diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, pregnancy, glucose intolerance, insulin resistance, bioactive compounds.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 FFS/Functional Food Science

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of their articles and grant the Functional Food Center (FFC) and its journals the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, including commercial use, provided the original author(s) and source are properly credited. Authors may post and share their published work freely, provided that the original publication in this journal is acknowledged.
By submitting to this journal, authors confirm that their manuscripts are original, not under consideration elsewhere, and that they hold the necessary rights to grant this license. The Functional Food Center encourages open scientific exchange and allows derivative and extended works, provided attribution to the original publication is maintained.