Blueberries and health
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/ffs.v2i1.875Abstract
Blueberry is a high value crop globally. Both wild and cultivated blueberries are commercially available to consumers. Although mostly consumed as fresh or frozen, dried blueberries are also offered in the market. Yogurts, beverages, jams, and jellies made with blueberries are some of the products popular with consumers.
Blueberries are rich in several health-beneficial phytochemicals including phenolic compounds and vitamins. This article reviews the health implications of blueberry consumption. The review was limited to the research studies published in peer-reviewed scientific journals. The impact of blueberry intake on cardiovascular functions, obesity, cancer, diabetes, cognitive performance, and gut microbiota was the focus of this review.
This review clearly revealed very broad health benefits of blueberry intake. However, it is evident that scientific studies on this topic are scarce. Indeed, there are only a few studies on the health effects of blueberries published in scientific journals. The majority of the investigations on this topic were carried out using animal models or cell cultures. Scarcity and limited size of the clinical studies in this field leave many questions about the effect of blueberry consumption on human health unanswered. Undoubtedly, there is a need for large-scale controlled and randomized clinical and epidemiological studies and meta-analyses of the data from such research. This would allow for an in-depth understanding of the effect of blueberries on health and the biological and metabolic pathways involved in disease mitigation and treatment.
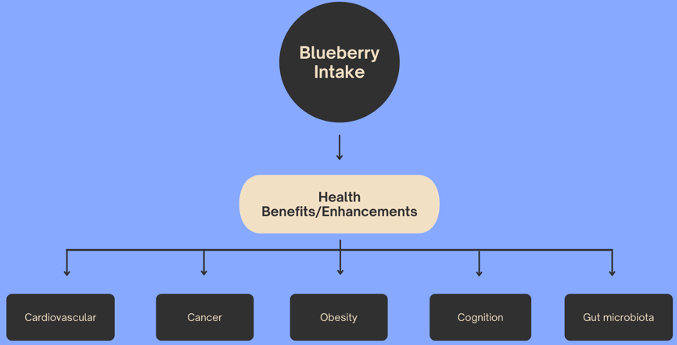
Keywords: Blueberry, cancer, cardiovascular health, chemical composition, cognitive performance, diabetes, gut microbiota, obesity, phytochemicals
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain the copyright of their articles and grant the Functional Food Center (FFC) and its journals the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, including commercial use, provided the original author(s) and source are properly credited. Authors may post and share their published work freely, provided that the original publication in this journal is acknowledged.
By submitting to this journal, authors confirm that their manuscripts are original, not under consideration elsewhere, and that they hold the necessary rights to grant this license. The Functional Food Center encourages open scientific exchange and allows derivative and extended works, provided attribution to the original publication is maintained.