Processing induced changes on coarse cereals (majorly millets) derived antioxidant compounds - a review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/ffs.v2i8.938Abstract
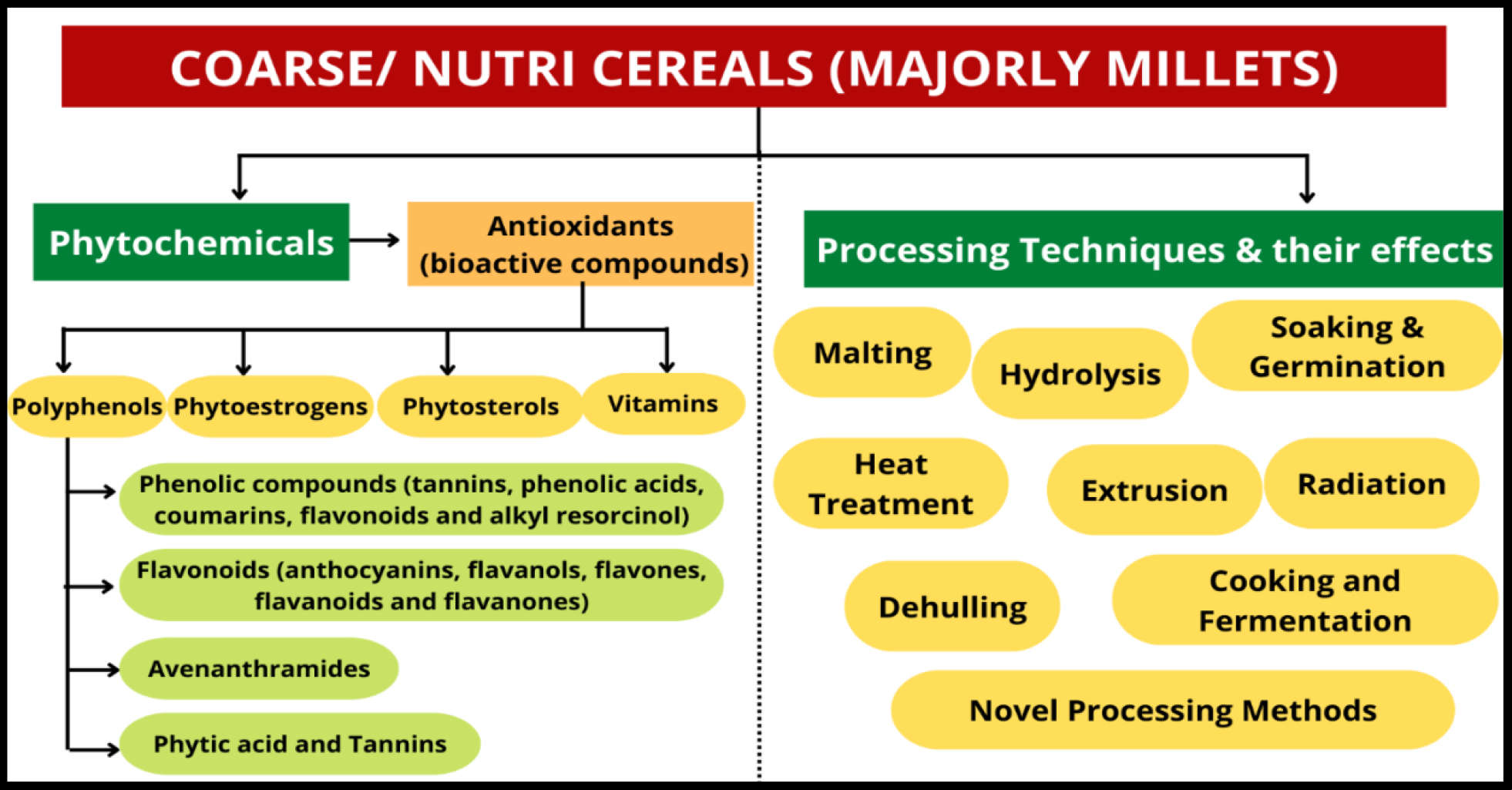
Coarse cereals also known as nutricereals contain several bioactive components that provide many health-promoting and disease-preventing properties. This paper presents a review of the effect of processing on the various antioxidant compounds present in coarse cereals. Polyphenols, phenolic compounds, flavonoids, tannins, avenanthramides, vitamins, and phytoestrogens are the major categories that contribute to the antioxidant properties of coarse cereals. As per the literature, processing technologies like fermentation, boiling, malting, hydrolysis, soaking and germination, heat treatment, microwaving and extrusion, etc, have a significant effect on these antioxidant compounds present in coarse cereals. Coarse cereals and their processed products could be of potential benefit to human health, but extensive research is required to optimize the dietary recommendation for realizing these health benefits.
Keywords: Millets; flavonoids; polyphenols, processing techniques
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain the copyright of their articles and grant the Functional Food Center (FFC) and its journals the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, including commercial use, provided the original author(s) and source are properly credited. Authors may post and share their published work freely, provided that the original publication in this journal is acknowledged.
By submitting to this journal, authors confirm that their manuscripts are original, not under consideration elsewhere, and that they hold the necessary rights to grant this license. The Functional Food Center encourages open scientific exchange and allows derivative and extended works, provided attribution to the original publication is maintained.