Acrylamide content and quality characteristics of French fries influenced by different frying methods
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/ffhd.v13i6.1126Abstract
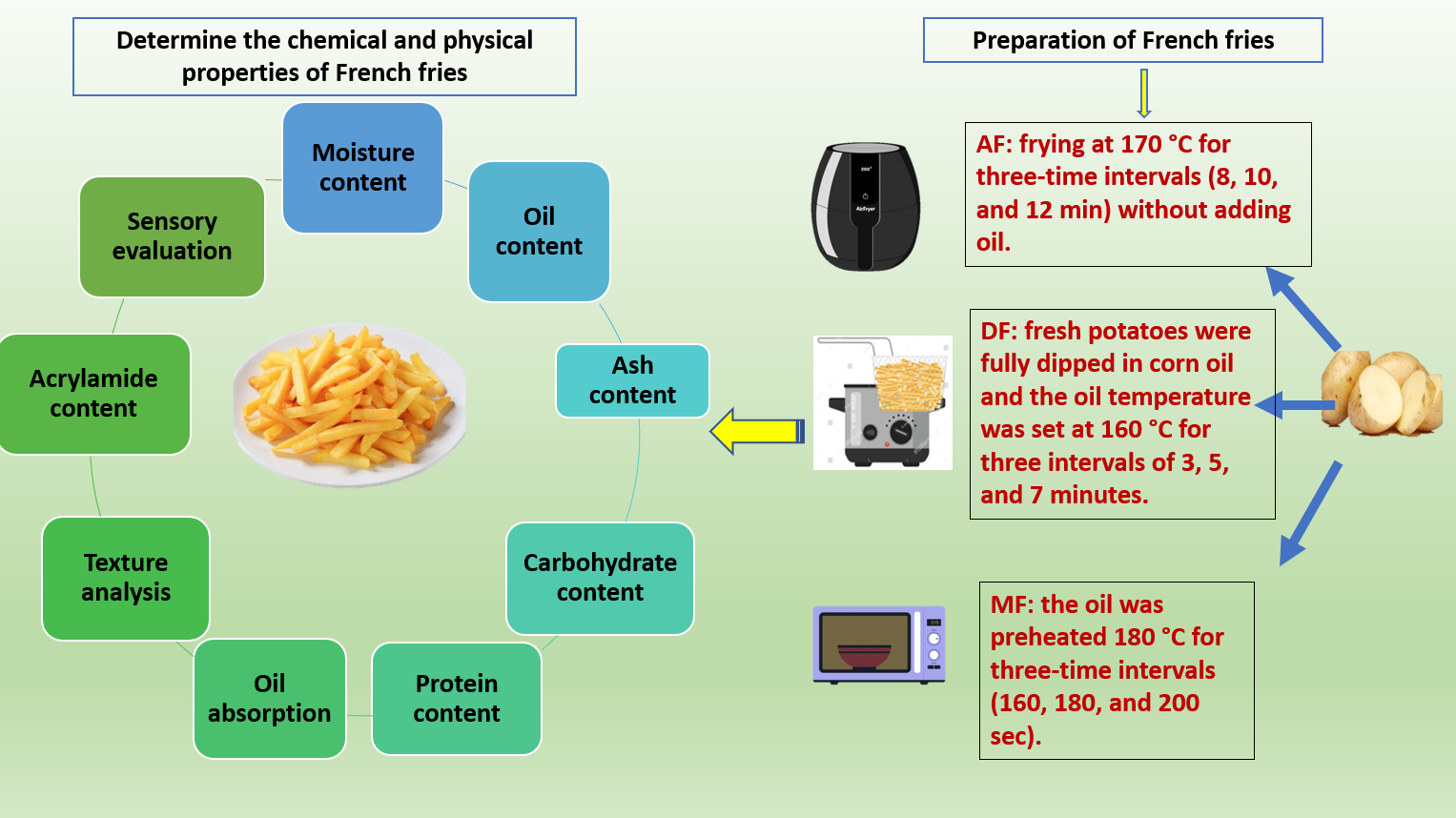
Background: This study aimed to compare the effects of three different frying methods, namely air frying (AF), microwave frying (MF), and deep frying (DF) in corn oil, on the moisture and texture, as well as the content and absorption of oil, carbohydrates and acrylamide in French fries.
Materials and Methods: For the DF, the fresh potatoes were fully dipped in corn oil and the oil temperature was set at 160 °C for three intervals of 3, 5, and 7 minutes. In the MF, the oil was preheated to 180 °C for three time intervals of 160, 180, and 200 seconds. The AF was set at a temperature of 170 °C for three time intervals of 8, 10, and 12 minutes, without adding oil.
Results: The results showed that AF resulted in a lower acrylamide content (21.8 ppm) after 8 minutes at 170°C compared to the other frying methods. However, DF in corn oil was preferred in terms of color, flavor, and overall acceptance in the sensory evaluation of the French fries. MF resulted in the hardest French fry texture due to excessive evaporation of moisture.
Conclusion: The findings suggest that AF may be a healthier option with a lower acrylamide content, while DF in corn oil may be preferred for its superior sensory characteristics.
Keywords: Acrylamide, Air frying, Deep frying, Microwave, Oil absorption, Sensory evaluation.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain the copyright of their articles and grant the Functional Food Center (FFC) and its journals the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, including commercial use, provided the original author(s) and source are properly credited. Authors may post and share their published work freely, provided that the original publication in this journal is acknowledged.
By submitting to this journal, authors confirm that their manuscripts are original, not under consideration elsewhere, and that they hold the necessary rights to grant this license. The Functional Food Center encourages open scientific exchange and allows derivative and extended works, provided attribution to the original publication is maintained.