In silico analyses of bioactive compounds extracted from ziziphus jujuba using supercritical CO2 extraction: Potential anti-anxiety and anti-Alzheimer’s disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/bchd.v6i10.1180Abstract
Background: Jujube (Chinese date) is a fruit with a pleasant, sweet taste, traditionally used as sedative to treat insomnia and anxiety.
Objective: The study aims to explore the potential of these bioactive compounds in exerting anti-anxiety and anti-Alzheimer's disease effects.
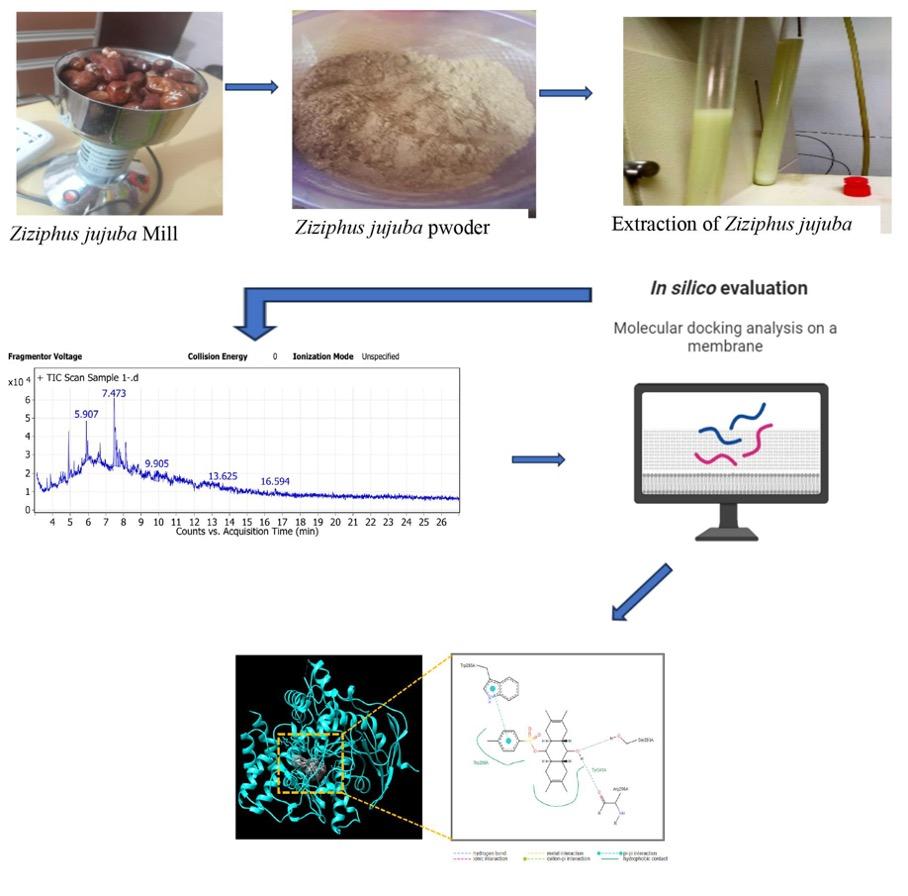
Methods: Molecular docking, ADME, and molecular dynamics studies were carried out for the green-extracted phytochemicals against acetylcholinesterase and Beta-amyloid proteins for Anti-Alzheimer’s disease effect and serotonin receptor for anti-anxiety activity. Our results suggest that compound (2,3,6,7-tetramethyl-10-(4-methylphenylsulfonyloxy)-1,4,4.alpha.,5,8,8a.beta.,9.b) showed good binding affinity of -10.3 with acetylcholinesterase (4EY7) as anti-Alzheimer’s disease and the compound andrographolide with serotonin transporter (6VRH) showed binding affinity of -9.7 for anxiety. Compounds with the best docking scores were subjected to molecular dynamic simulations.
Results: These compounds revealed the best stability.
Conclusion: These findings are promising for manufacturing new functional foods, nutraceuticals, food supplements, and/or pharmaceuticals which may play a good and safe role in treating Alzheimer disease and anxiety. While further biological studies must be carried out, our computational studies suggest that these compounds have potent activity.
Keywords: Ziziphus jujuba; Bioactive compounds; Neurological disorders disease; Molecular docking, ADME and Molecular dynamics.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain the copyright of their articles and grant the Functional Food Center (FFC) and its journals the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, including commercial use, provided the original author(s) and source are properly credited. Authors may post and share their published work freely, provided that the original publication in this journal is acknowledged.
By submitting to this journal, authors confirm that their manuscripts are original, not under consideration elsewhere, and that they hold the necessary rights to grant this license. The Functional Food Center encourages open scientific exchange and allows derivative and extended works, provided attribution to the original publication is maintained.