Baicalin: A potential therapeutic agent for diabetes and renal protection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/bchd.v6i9.1148Resumé
Background: Diabetes is a complex metabolic disease manifested by raised glucose levels in the blood and impaired insulin function leading to various organ complications, including diabetic nephropathy. Baicalin, a flavonoid derived from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, has garnered substantial attention for its diverse beneficial effects, including anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti- apoptotic properties, etc. Intriguingly, in vivo studies in rats have further unveiled baicalin’s potential to directly modulate pancreatic beta cells, suggesting a promising role as an anti-diabetic agent.
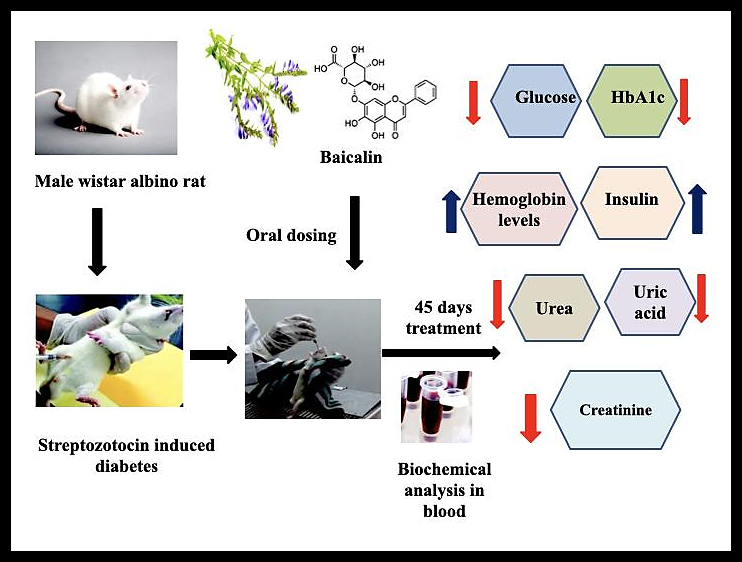
Objective: The purpose of this study is to comprehensively explore the anti-diabetic effect of baicalin, focusing on key parameters such as plasma insulin levels, glucose levels, hemoglobin, and glycated hemoglobin levels in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Additionally, we sought to explore Baicalin’s ability to provide renal protection by evaluating serum renal markers.
Methodology: This study involved a total of 30 Wistar albino male rats. Diabetes was created in rats by a single intraperitoneal streptozotocin injection (40 mg/kg). After 72 hours, the rats with diabetes were segregated into four treatment groups (Group II to Group V) comprising 6 animals each. Group I consists of six normal control rats (without diabetes). The groups received different treatment protocols, including normal saline, DMSO, Baicalin (50 mg/kg/day), and glibenclamide (6 mg/kg/day) for 45 days. Throughout the study, meticulous observations were made regarding the animals’ general appearance, body weight, behavior, and their fasting glucose levels in venous blood.
Results: Oral dosing with Baicalin at the rate of 50 mg/kg body weight revealed notable enhancements in insulin secretion and hemoglobin levels, alongside notable reductions in blood levels of glucose and glycated hemoglobin compared to the glibenclamide-treated type 2 diabetic rats. Additionally, Baicalin displayed a protective action on renal tissue, as shown by reduced serum creatinine, uric acid, and urea levels.
Conclusion: Our investigation unveils Baicalin’s potential as a promising anti-diabetic agent with the added benefit of renal tissue protection. The observed improvements in various physiological parameters warrant further exploration of Baicalin’s therapeutic mechanisms and clinical applications, presenting it as a compelling candidate for diabetes management and diabetic nephropathy prevention.
IAEC Approval No: AVMC/IAEC/2019/07/25/08
Keywords: Baicalin, Blood glucose, Diabetes, Male wistar rats, Streptozotocin
Downloads
Publiceret
Nummer
Sektion
Licens
Ophavsret (c) 2023 FFC/Bioactive Compounds in Health and Disease

Dette værk er under følgende licens Creative Commons Navngivelse –Ikke-kommerciel (by-nc).
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.