A simplified HPLC-UV method for the analysis of triterpenoid acids from heritage apples (Malus domestica) from western North Carolina, USA
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/bchd.v5i4.914Abstract
Background: Pentacyclic triterpenoid acids are common in a number of food and spice plant species. Apples (Malus domestica) are the most common human food source for these potentially beneficial phytochemicals. Pre-20th century heritage apples have long been grown in mountainous western North Carolina and may be a wide-ranging source of these phytochemicals.
Objectives: Existing extraction and analytical methods were improved and used to assess the content of three triterpenoid acids in heritage apple cultivars grown in western North Carolina, USA.
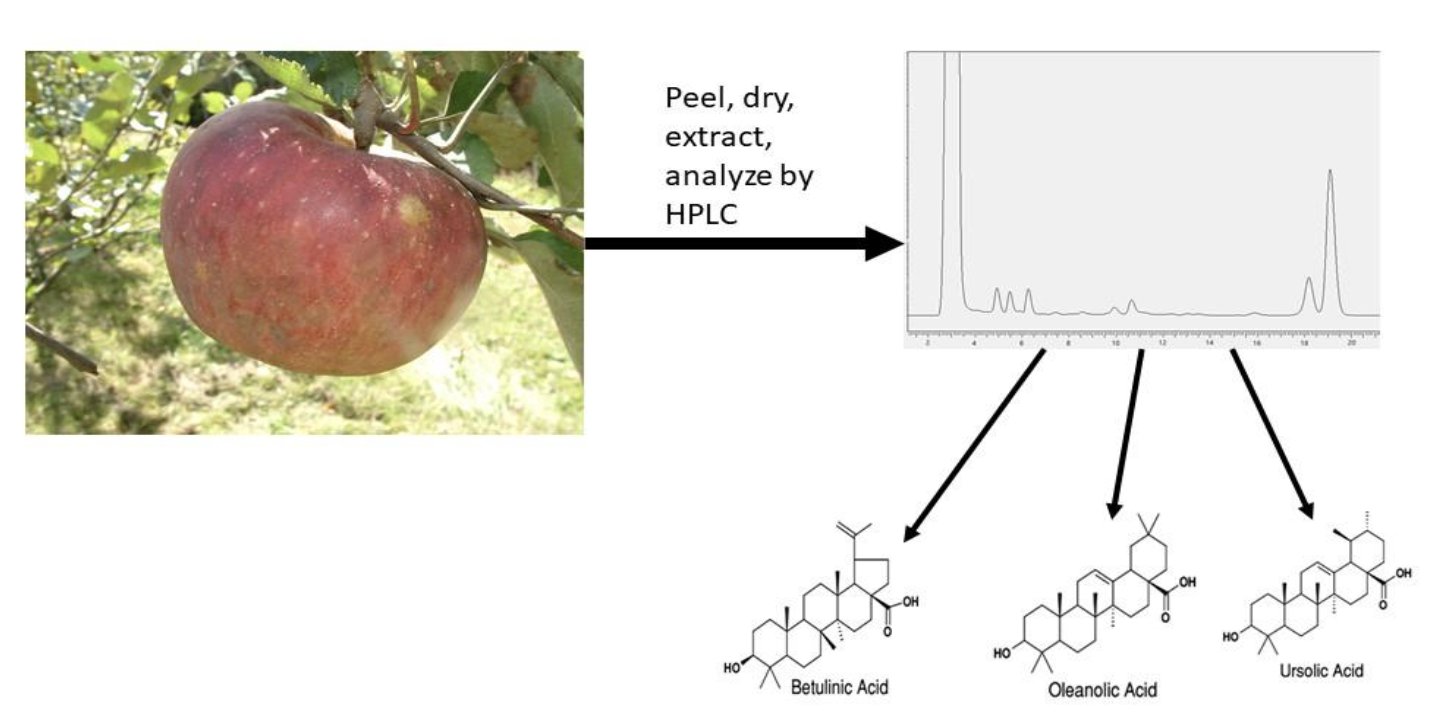
Methods: Apples from a local farmers market were collected during the fall apple season. Apple peels were freeze dried, ground, and extracted with ethanol thrice. Extracts were analyzed by HPLC against external standards for betulinic, oleanolic, and ursolic acids.
Results: The improved method was used to extract and to analyze the triterpenoid acid levels in 16 heritage apple cultivars grown in the Appalachian region of western North Carolina. Total triterpenoid acids ranged from 2 to 29 mg/g dry weight of peels. Content did not vary by apple color or time of harvest. Russeted varieties contained noticeably less triterpenoids.
Conclusions: An improved and simplified method was used for the analysis of heritage apple varieties in western North Carolinas. A wide range of values was found for these compounds of increasing interest in the human diet and in human health.
Keywords:apples, phytochemicals, triterpenoids, ursolic acid, Appalachia
Veröffentlicht
Ausgabe
Rubrik
Lizenz
Copyright (c) 2022 FFC/Bioactive Compounds in Health and Disease

Dieses Werk steht unter der Lizenz Creative Commons Namensnennung - Nicht-kommerziell 4.0 International.
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.