The effects of Membrane Lipid Replacement with NTFactor® Lipids on increasing the bioavailability of three test nutrients
DOI :
https://doi.org/10.31989/bchd.v5i5.936Résumé
Introduction: Previous studies indicated that lipids and nanostructured materials may improve the uptake of nutrients with moderate bioabsorption properties.
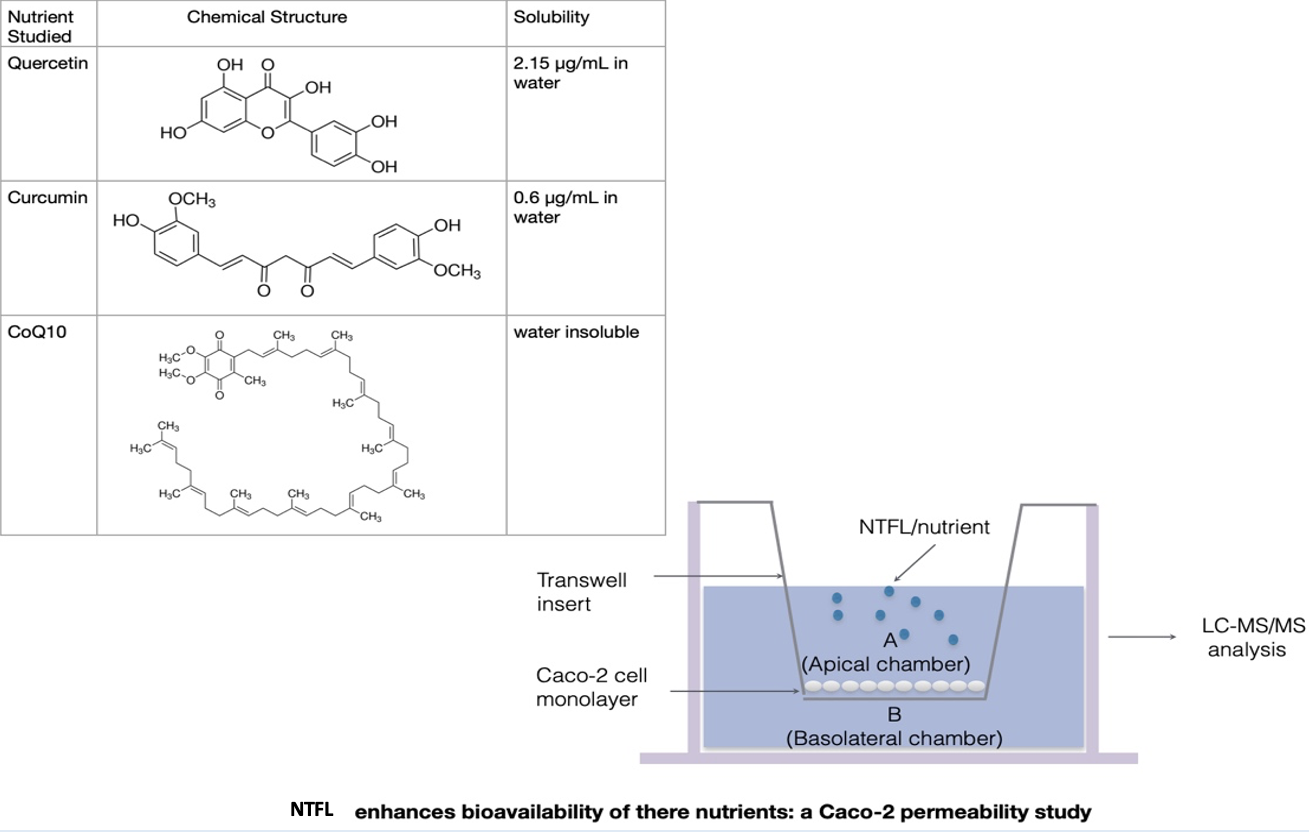
Objectives: This study evaluated the effects of Membrane Lipid Replacement with NTFactor® Lipids (NTFL) on bioabsorption of three poorly to moderately absorbed nutrients (quercetin, curcumin and coenzyme Q10) utilizing the Caco-2 epithelial cell permeability model.
Methods: Transfer across a Caco-2 epithelial cell layer has become a reference standard in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries for in vitro prediction of in vivo human intestinal absorption and bioavailability of orally administered substances. The degree of bioabsorption of the test materials was assessed by monitoring the concentrations of the test materials on each side of the Caco-2 monolayers by liquid chromatography and mass spectroscopy (LCMS/MS analysis).
Results: When NTFL was added to each of the three test nutrients, there was increased absorption and transfer across a Caco-2 cell layer in a dose-dependent manner for the three nutrients. When compared individually, CoQ10 with NTFL showed the most significant increase in absorption (2.01-times more compared to controls without NTFL, p=0.0011) at a concentration of NTFL of 10 mg/mL. NTFL also increased absorption and transfer across a Caco-2 cell layer of the other test nutrients, but these results did not achieve the same level of significance.
Discussion: A variety of Oral membrane lipid replacement supplements with NTFL, such as various vitamins, minerals and nutrients, have been designed to reduce fatigue, improve health conditions, and protect cellular and especially mitochondrial membranes from damage. Here we used NTFL to demonstrate improvements in absorption and bioavailability of three nutrients.
Conclusion: Using the Caco-2 bioabsorption and bioavailability in vitro model we found that NTFL could enhance absorption, bioavailability and uptake of nutrients while providing its own clinically demonstrated health benefits.
Keywords: Phospholipids, Membrane Lipid Replacement, CoQ10, curcumin, quercetin, bioavailability, absorption, permeability, Caco2, bio-uptake, bioabsorption, glycerolphospholipids, intestinal absorption
Téléchargements
Publié
Numéro
Rubrique
Licence
© FFC/Bioactive Compounds in Health and Disease 2022

Cette œuvre est sous licence Creative Commons Attribution - Pas d'Utilisation Commerciale 4.0 International.
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.