Hepatoprotective effect of morin via regulating the oxidative stress and carbohydrate metabolism in STZ induced diabetic rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/bchd.v5i3.893Resumo
Background: Diabetes mellitus is widely recognized as one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. Hyperglycaemia-mediated oxidative stress plays a significant role in the development and progression of diabetes - induced liver damage.
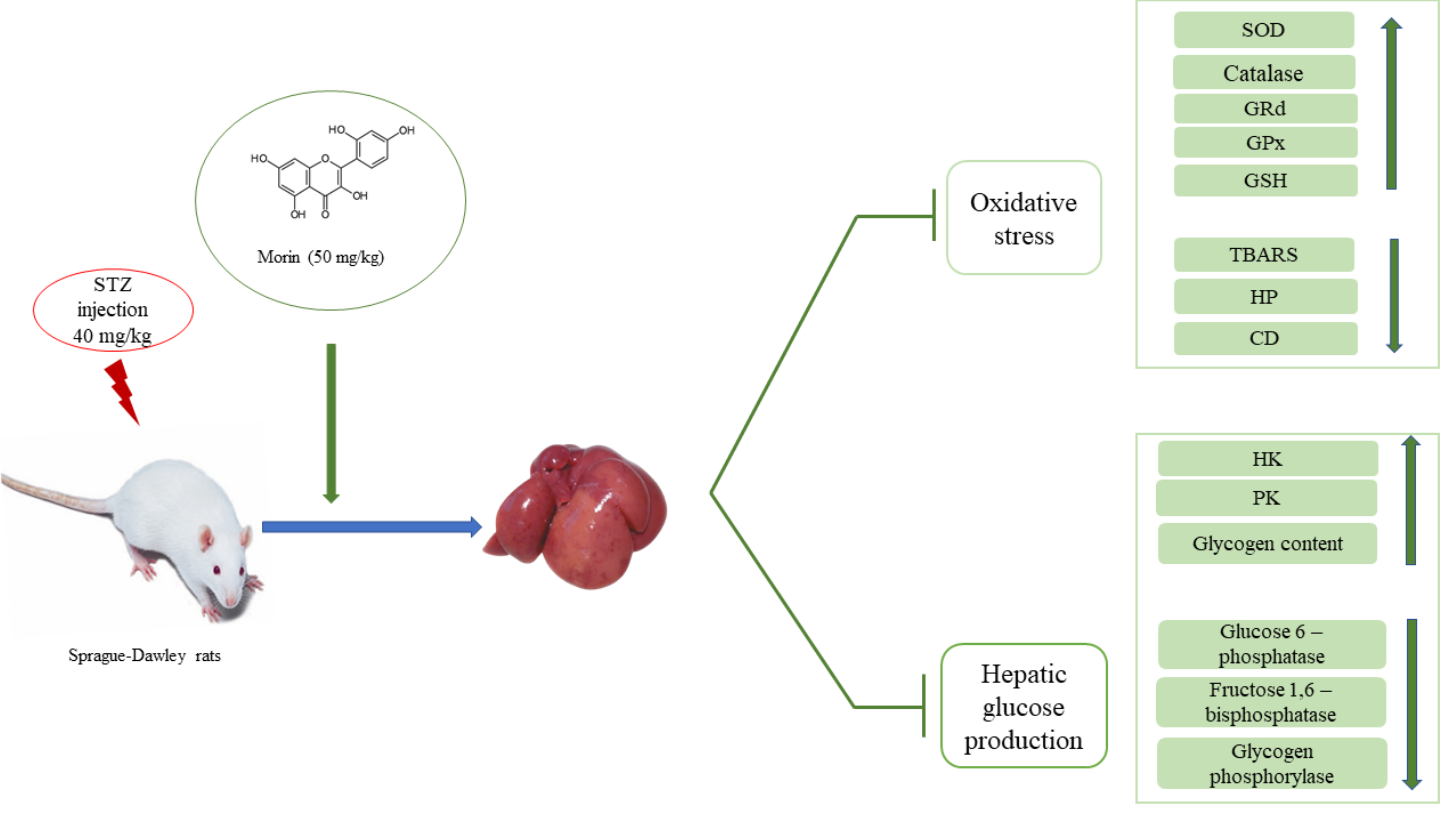
Objective: The main aim of the study was to explore the modulatory effect of the flavonoid morin (3,5,7,2’,4’ -pentahydroxyflavone) on oxidative stress and carbohydrate metabolism in the liver of streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetic rats.
Methods: Diabetes was induced in male albino rats by intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (40 mg/kg body weight) and subsequently, the animals were given morin intragastrically at a dose of 50 mg/kg body weight for 60 consecutive days. At the end of the treatment period, the animals were sacrificed by an intraperitoneal injection of thiopentone sodium. Blood and liver tissue were collected for further biochemical evaluation and the effects were compared with diabetic rats administered metformin, a standard antidiabetic drug.
Results: Elevated blood glucose and HbA1c levels in diabetic rats were significantly decreased by morin administration. Morin effectively modulated the alternations in the concentration of lipid peroxidation products, activities of antioxidant enzymes and carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes in the liver of diabetic rats. The overall effects were comparable with diabetic rats administered with metformin.
Conclusion: The results of our study proved that the morin administration exerts hepatoprotective activity by decreasing oxidative stress and regulating the altered activities of carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes in diabetes.
Keywords: diabetes, morin, liver, oxidative stress, carbohydrate metabolism
Downloads
Publicado
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2022 FFC/Bioactive Compounds in Health and Disease

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.