Nutritional supplements for athletes and personalization; a short review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/ffs.v2i10.993Abstract
The main argument for the optimization of nutritional strategies in athletes, besides improved performance, is the preservation of health and the prevention of unwanted training effects. This highlights the importance of personalized nutrition strategies, as well as functional foods and phytonutrients based on individual requirements which can be precisely defined by detailed analyses, including genetics, epigenetics, gut microbiota, gender, and environmental factors. Recently, a miRNA-based “Fitness Score to Assess the Individual Response to Diet, Metabolism and Exercise” was developed by our group. Formulations of sports drinks and sports foods should be carefully considered, as they frequently contain a mixture of multiple ingredients. Macronutrient supplements, such as carbohydrates, proteins, protein components, fatty acids and probiotics are known to provide benefits for athletes with energy deficits, electrolyte imbalance, gastrointestinal issues, fatigue, and cardiovascular problems. However, micronutrient supplements, such as vitamins, minerals, trace elements and ergogenic aids (e.g., caffeine) must be administered in specific doses based on individual need. Considering the novel data on inter-organ communication (e.g., gut-muscle-brain-axis), data from systems biology highlight the importance of holistic aspects, where nutrients and probiotic supplements are gaining importance for improved performance, reduced risks of illness/ injury and enhanced recovery.
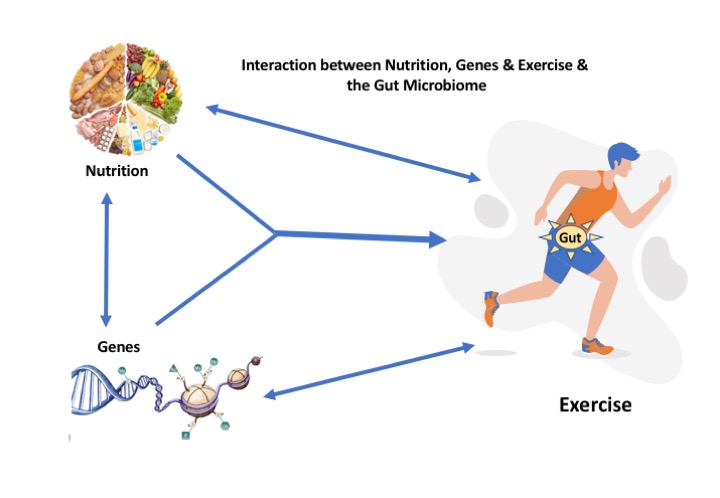
Keywords: Nutrition, additives, functional foods, exercise, microbiome, epigenetics, personalization
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.