In vitro assessment of thrombolytic potential of red and white ginger (Zingiber officinale)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/ffhd.v14i1.1245Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a leading cause of death, and their pathogenesis is commonly attributed to thrombosis. Although existing medications are effective and fast-acting for thrombosis management, they tend to be expensive and cause severe side effects. Plant-based thrombolytic agents are actively sought after as inexpensive and safe alternatives for the treatment and prevention of thrombosis. Red ginger (Zingiber officinale var. rubrum) and white ginger (Zingiber officinale var. officinale) are widely used in foods and beverages and are believed to confer a wide variety of health benefits.
Objective: This study aims to elucidate the thrombolytic and fibrinolytic potential of red and white ginger extracts in vitro.
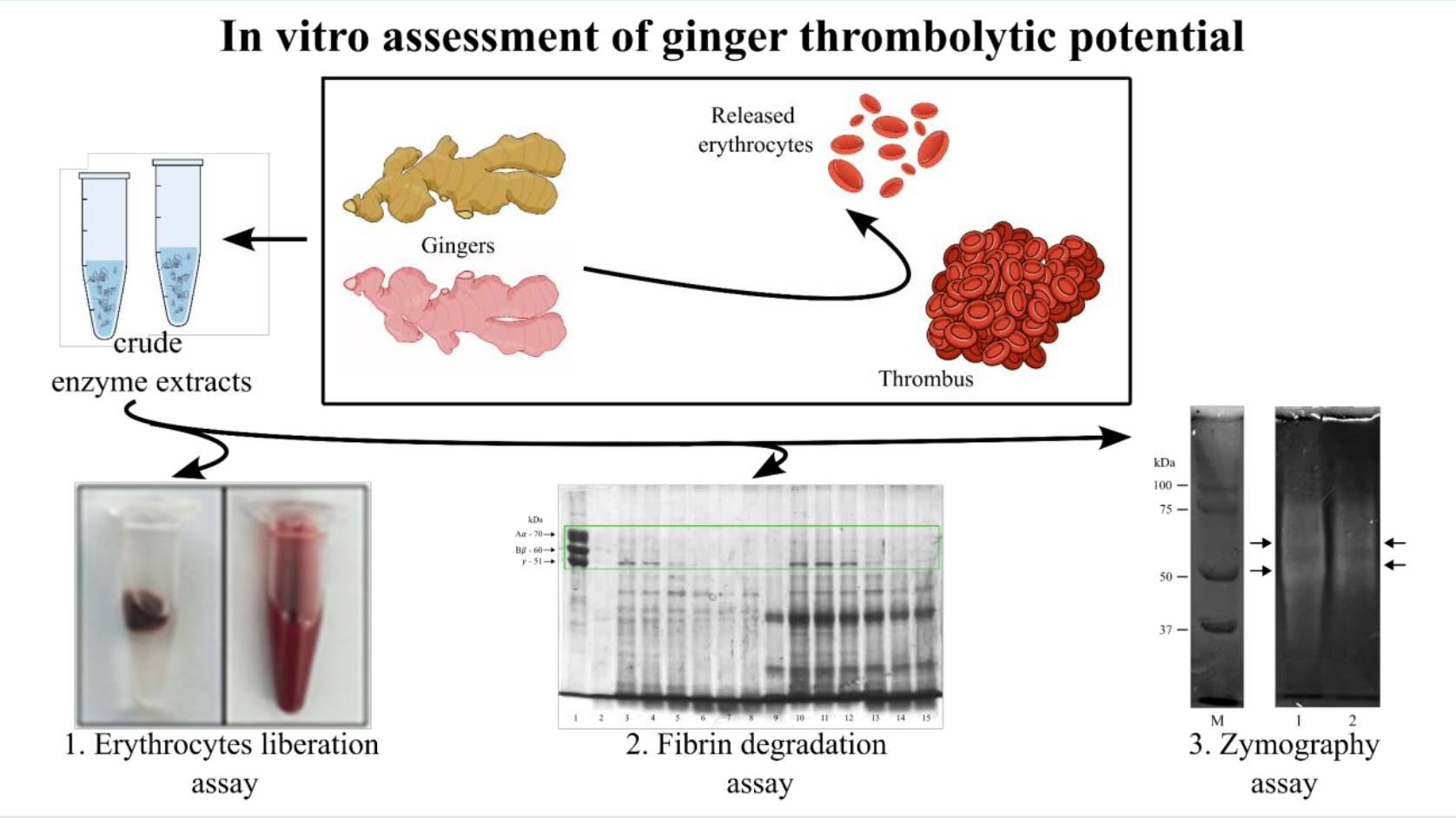
Methods: In this study, in vitro analyses were performed using erythrocyte liberation, euglobulin degradation, fibrin degradation, and fibrin zymography assays. The ability of crude enzyme extracts from both red (rgEx) and white ginger (wgEx) to degrade blood clots was analyzed using the erythrocytes liberation assay. Then, the thrombolytic and fibrinolytic activities of rgEx and wgEx were evaluated using euglobulin and fibrin degradation assays, both of which were visualized using Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Finally, fibrinolytic enzymes were identified using a fibrin zymography assay.
Results: Red and white ginger extracts were found to have strong thrombolytic properties via high total liberated erythrocyte count from the erythrocyte liberation assay. The ginger extract proteases can rapidly degrade euglobulin and fibrin, with their priority order beginning with Aα and Bβ, then γ chains. Fibrin zymography confirmed the presence of several proteases in the red and white ginger extracts.
Conclusion: Overall, while red and white ginger crude enzyme extracts have been reported to possess a strong thrombolytic and fibrinolytic potential and are therefore suggested to be good candidates for managing and preventing CVD, further studies such as full enzyme identification and in vivo studies are needed.
Keywords: fibrinolytic, ginger extract, in vitro assessment, protease, thrombolytic
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain the copyright of their articles and grant the Functional Food Center (FFC) and its journals the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, including commercial use, provided the original author(s) and source are properly credited. Authors may post and share their published work freely, provided that the original publication in this journal is acknowledged.
By submitting to this journal, authors confirm that their manuscripts are original, not under consideration elsewhere, and that they hold the necessary rights to grant this license. The Functional Food Center encourages open scientific exchange and allows derivative and extended works, provided attribution to the original publication is maintained.