Correction of metabolic disturbances by functional food compositions in experimental obesity in CD-1 and agouti-yellow mice
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/ffhd.v12i1.874Abstract
Background: To determine the most promising composition, the possibility of correction of metabolic disturbances was investigated with the use of functional food compositions in CD1 and agouti-yellow mice in experimental obesity.
Methods: Agouti-yellow and CD1 mice were divided into 10 groups (control, 1/1, 1/9, 2/1, 2/9 in each line) according to diets. For 4 weeks, the groups ate a high-calorie diet. Starting with week 5th, composition 1 was added to the diet in groups 1/1 (60% lard + 39% standard laboratory feed + 1% composition 1 + 10% fructose solution), 1/9 (60% lard + 31% standard laboratory feed + 9% composition 1 + 10% fructose solution); composition 2 was added to the diet in groups 2/1 (60% lard + 39% standard laboratory feed + 1% composition 2 + 10% fructose solution), 2/9 (60% lard + 39% standard laboratory feed + 9% composition 2 + 10% fructose solution). On the day 56th, each animal was weighed, blood was taken for biochemical analysis (glucose, LDL, cholesterol and HDL) and organs (the skin of the anterior abdominal wall, skeletal muscle tissue in the area of the lateral surface of the thigh, liver, kidneys with perirenal tissue, pancreas, and thymus) were taken for histological examination.
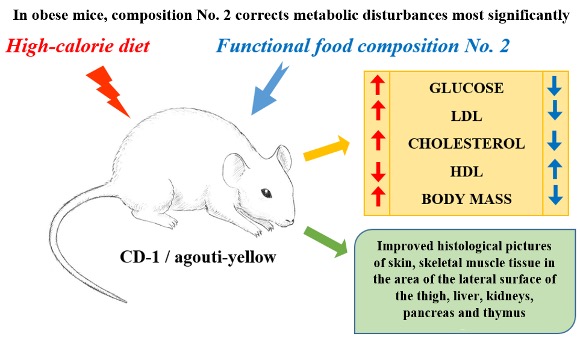
Results: In agouti-yellow mice, group 2/9, the greatest decrease in blood glucose level was observed compared to the control group by 34.6% (p < 0.05). Consumption of compositions in groups 1/9 and 2/9 led to a significant decrease in LDL and a significant decrease in total cholesterol level by 21.9% (p < 0.05) and 18.8% (p < 0.05) respectively compared to the control group. HDL was significantly higher in groups 1/9, 2/9 than in the control group. In CD-1 mice, group 2/9 showed the best result in glucose level (mean 5.78 mmol/l) among all groups receiving functional food compositions and the control group. The most pronounced decrease in LDL was observed in groups 1/9, 2/9 compared to the control group (p < 0.05). HDL value in group 2/9 significantly exceeded the mean value in the control group, by 54.8% (p < 0.05). Body mass of agouti-yellow mice and CD-1 mice in groups 1/1, 2/1, 1/9, and 2/9 significantly decreased compared to control groups. According to the results of histological examination of organs and tissues, functional food composition 2 turned out to be the most promising.
Conclusion: According to the results of the study, the most promising composition was selected (composition 2). Feeding animals with this composition improved histological pictures of studied organs and tissues, biochemical blood parameters and effectively reduced body mass in both experimental animal lines, CD-1, and agouti-yellow mice, compared to the control groups.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.