Lime peel as a potential functional ingredient for chronic inflammation treatment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/bchd.v6i7.1136Περίληψη
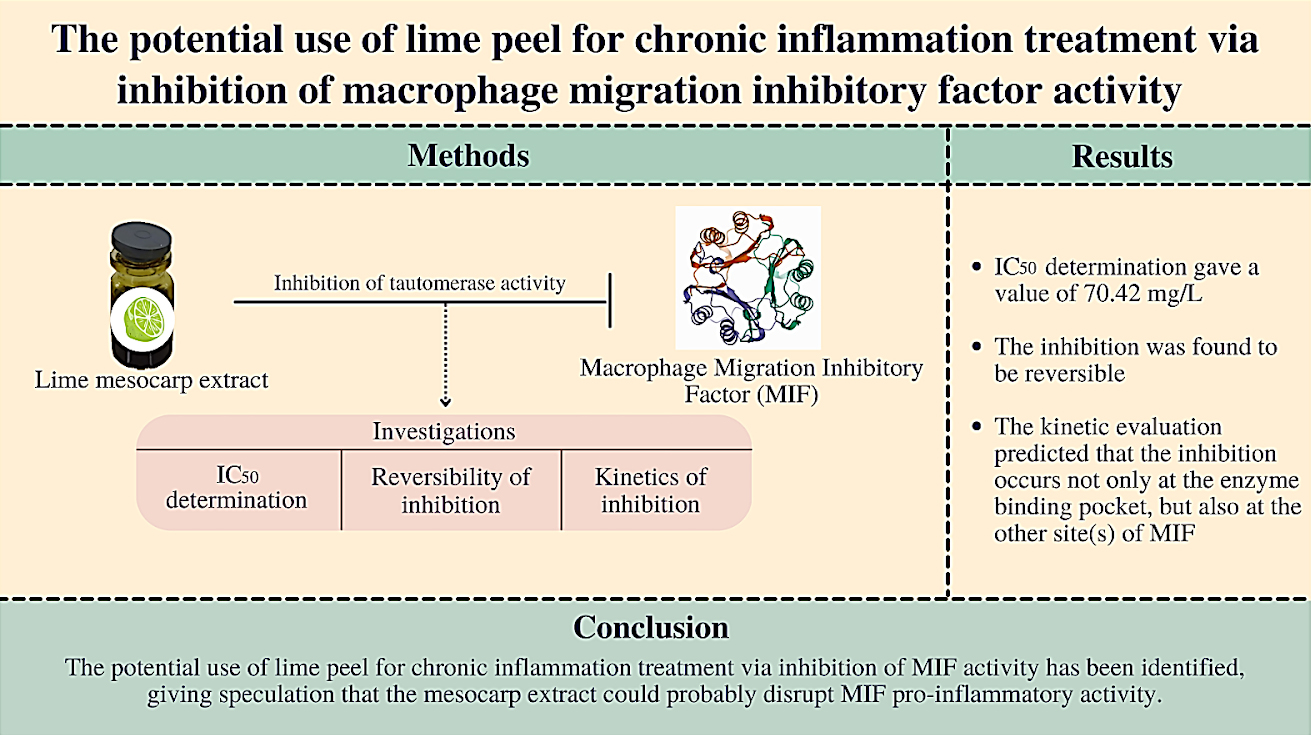
Background: Lime peel, derived from Citrus aurantifolia Swingle, is an ingredient that is frequently discarded despite possessing exceptionally high functional food properties. It contains phytochemicals with health-promoting properties, several of which are reported to have anti-inflammatory properties. However, the specific mechanisms underlying their anti-inflammatory properties have not been elaborated. This study aimed to evaluate the potential use of lime peel as a functional food ingredient for chronic inflammation treatment via the inhibition of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) activity. MIF is a pro-inflammatory mediator that plays a vital role in the progression of inflammation. This activity of MIF is associated with the pathogenesis of chronic inflammation.
Methods: The inhibition of MIF activity could be used as an approach to identify the potential use of a functional food ingredient for chronic inflammation treatment. This study focused on the investigation of the inhibitory potential, reversibility, and kinetics of lime mesocarp extract on MIF tautomerase activity.
Results: The results showed that the lime mesocarp extract can inhibit MIF tautomerase activity with an IC50 of 70.42 mg/L in a reversible manner, demonstrating its safe potential for use. The kinetic evaluation predicted that the inhibition occurs not only at the enzyme binding pocket but also at the other site(s) of MIF, speculating the possibility of disruption in MIF pro-inflammatory activity.
Conclusion: The potential safe use of lime peel as a functional food ingredient for chronic inflammation treatment has been identified.
Keywords: Lime peel, functional food ingredient, chronic inflammation, macrophage migration inhibitory factor, reversible inhibitor.
Δημοσιευμένα
Τεύχος
Ενότητα
Άδεια
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.