Sensory characteristics of selective traditional Indian sweets using agave syrup and stevia : An observatory study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/ffhd.v12i12.1042Abstract
Background: Indian sweets largely contribute to the rising graph of obesity and cardiovascular diseases in India. An urgent update in lifestyle and dietary patterns has become necessary to stay risk-free. Replacement of sucrose with natural sweeteners in traditional Indian sweets is one way of dealing with the consequences of high sucrose consumption. This study tries to understand the change in sensory characteristics of selective Indian sweets on the replacement of sucrose with natural sweeteners like Agave syrup and Stevia.
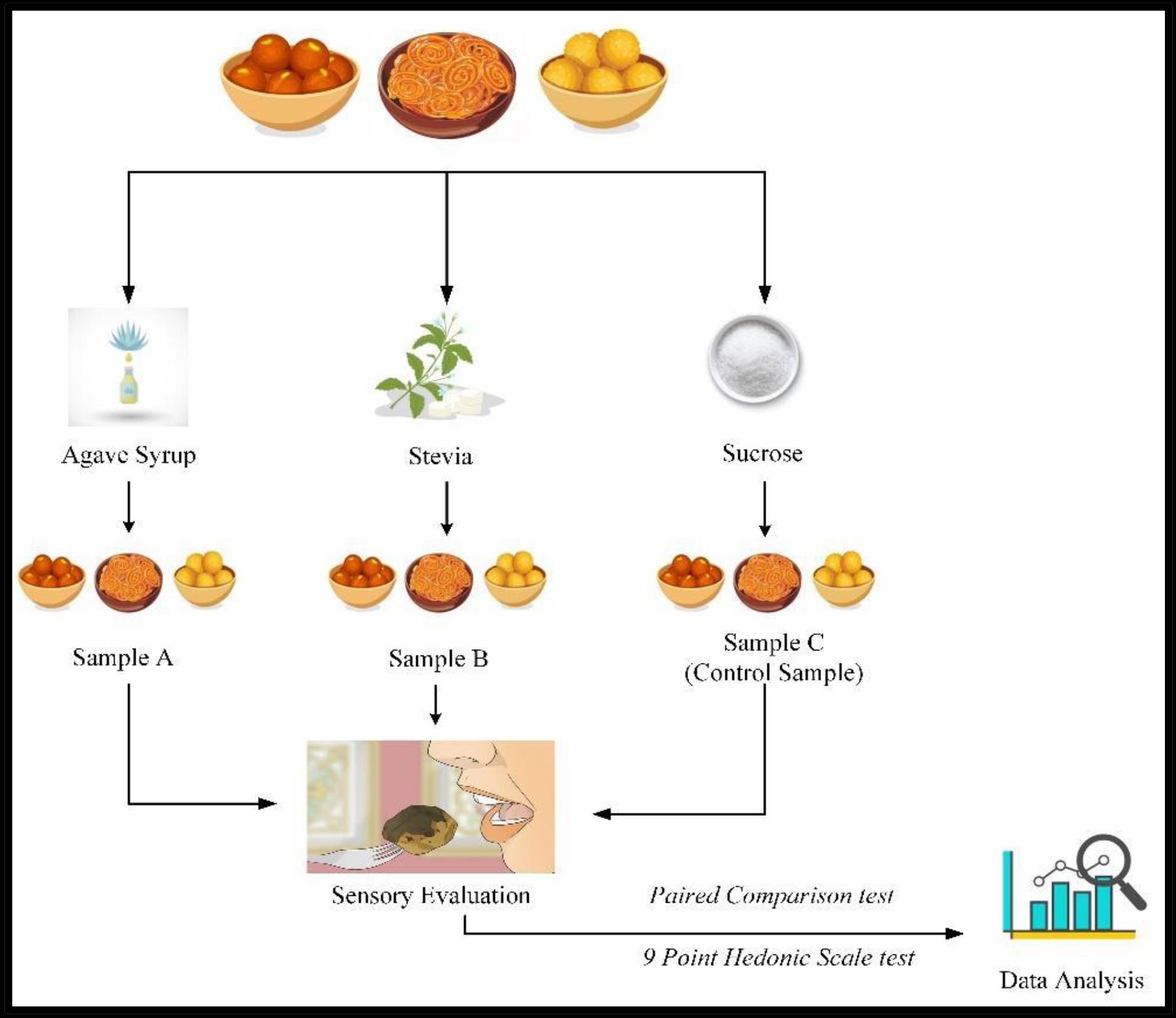
Objectives:In this observatory study, sensory characteristics of traditional Indian sweets (Gulab Jamun, Jalebi, and Motichoor Ladoo) are observed after sucrose replacement with natural sweeteners.
Methods:In order to examine the flavour and appearance of selected Indian sweets, sucrose is substituted with agave syrup and stevia. Product characteristics namely appearance, flavour, colour, odour, aftertaste, and overall acceptability of the standardized sweets are compared with the control samples prepared with sucrose.
Results: Results using the 9-point hedonic scale conclude that out of the two natural sugars used as a substitute for sucrose, stevia showed better overall acceptability for Gulab Jamun (84%) and Motichoor Ladoo (59%), but not for Jalebi (30%). Results for the paired comparison test conclude that substituting Agave syrup with sucrose had an undesirable effect on colour, taste, and mouthfeel while substituting Stevia had a detrimental effect on taste and mouthfeel only.
Conclusion:The results conclude an initial understanding of sucrose replacement using natural sugars namely Stevia and Agave syrup in the context of traditional Indian sweets and Stevia is better-suited replacement in Gulab Jamun.
Keywords: Natural sweeteners, Sucrose replacement, Indian sweets, Sensory evaluation, new product development, Agave syrup, Stevia
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain the copyright of their articles and grant the Functional Food Center (FFC) and its journals the right of first publication under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, including commercial use, provided the original author(s) and source are properly credited. Authors may post and share their published work freely, provided that the original publication in this journal is acknowledged.
By submitting to this journal, authors confirm that their manuscripts are original, not under consideration elsewhere, and that they hold the necessary rights to grant this license. The Functional Food Center encourages open scientific exchange and allows derivative and extended works, provided attribution to the original publication is maintained.