Authors
-
Junyoo Takizawa
MAINICHIEGAO.CO.,LTD.
-
Asami Baba
ORTHOMEDICO Inc.
-
Tsuyoshi Takara
Medical Corporation Seishinkai, Takara Clinic
Abstract
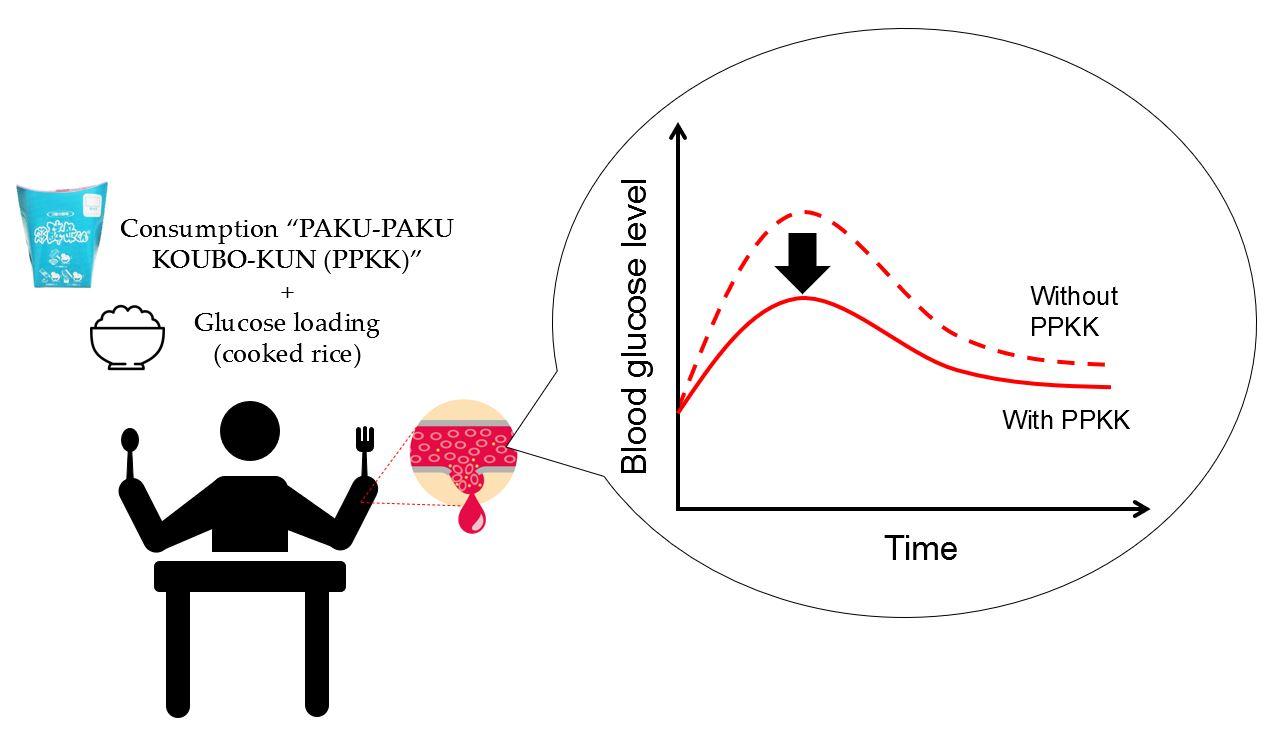
Objective: This study’s purpose was to verify the PAKU-PAKU KOUBO-KUN (PPKK) containing yeast and mulberry extract concentrate’s effects on suppressing elevated postprandial blood glucose (PBG).
Methods: Two randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover studies (TRIAL-1 and TRIAL-2) were conducted. Both studies included healthy Japanese adults with a maximum PBG concentration (Cmax) in the range of 140–199 mg/dL. Study subjects were randomly assigned to take PPKK or placebo food. Then subjects consumed 200 g of cooked rice within 10 minutes of test food consumption. Blood glucose (BG) levels were evaluated before intervention, and 30 min, 60 min, 90 min, and 120 min after consumption. The main endpoint was the incremental area under the curve (IAUC) of PBG.
Results: The analysis included 36 subjects in TRIAL-1 and 41 subjects in TRIAL-2. A combined analysis (n = 71) was conducted. Both individual studies and combined analysis showed that PPKK significantly reduced the IAUC of PBG. In particular, BG levels were significantly lower at 30 min, 60 min, and 90 min after intervention. No adverse effects were identified.
Conclusions:These results indicated that PPKK moderated the increase in PBG and enhanced glucose metabolism.
Trial registration: UMIN-CTR: UMIN000042445 and UMIN000045341
Foundation: Mainichiegao Co., Ltd.
Keywords: postprandial blood glucose, yeast, mulberry, prediabetes, glycemic control
Author Biographies
-
Junyoo Takizawa, MAINICHIEGAO.CO.,LTD.
Junyoo Takizawa is the president of MAINICHIEGAO.CO., LTD. He graduated in 1999 at the Department of Politics, Faculty of Law, HOSEI University. From 1999 to 2003, he was in charge of event planning, production and management at an advertising agency. Then, from 2003 to 2005, he was in charge of product planning, advertising, and order management for a health food product electronic commerce company. In 2005, he founded the electronic commerce company for health food products, MAINICHIGENKI.CO., LTD. Later in 2011, he founded the electronic commerce company for health food products, MAINICHIEGAO.CO., LTD. He is interested in the researches on the effects of nucleic acid on cognitive function, yeast on blood sugar, Sedum sarmentosum on liver function, Salvia miltiorrhiza on blood vessels, Golden sea cucumber (Cucumaria japonica) on cartilage of knee joint, and sake lees & Hemerocallis fulva on sleep. He has been the Executive Director, Committee on Chinese Medicine of World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies since 2016.
-
Asami Baba, ORTHOMEDICO Inc.
Asami Baba (PhD) is the manager of the Clinical Science Division at ORTHOMEDICO Inc. She graduated in 2016 at the Department of Pediatrics, Graduate School of Medicine, Nippon Medical School. After graduation, she joined ORTHOMEDICO Inc. and has been responsible for designing and interpretation of results of clinical trials of foods on human. Her current and previous research interests are antioxidative effect of foods, and evaluation of food functionality. She is member of 1) Japan Society for Dementia Research, 2) Japan Society for Early Stage of Dementia, 3) Japan Society of Nutrition and Food Science, and 4) Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Agrochemistry. She also received Young Scientist Award of 18th Japan Society for Early Stage of Dementia.
-
Tsuyoshi Takara, Medical Corporation Seishinkai, Takara Clinic
Tsuyoshi Takara (MD) is the director of Medical Corporation Seishinkai, Takara Clinic. He graduated in 1985 at St. Marianna University School of Medicine. From 1985 to 1991, he worked at the First Department of Surgery, St. Marianna University School of Medicine. Then, from 1991 to 1995, he worked at McGill University Hospital Center, McGill, Quebec, Canada. Afterward, from 1995 to 2002, he worked at the Department of Surgery, Japan Labour Health and Welfare Organization, Kanto Rosai Hospital. Later in 2002, he opened Cebu Medical Clinic. 4 years later in 2006, he changed the name of the said clinic to Takara Clinic. His current and previous research interests are immunotherapy, and evaluation of food functionality. He is member of the Japanese Society of Anti-aging Medicine, and the Society for Integrative Medicine Japan.
Section
Research Articles
License
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.