Phytochemicals in commonly consumed foods in malawian diets
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31989/ffhd.v12i10.976Abstract
Background: Plant foods, as functional foods, provide not only the essential nutrients needed to sustain life, but also bioactive compounds (phytochemicals) for health promotion and disease prevention.
Objective of the study: The aim of this research was to screen phytochemicals in commonly consumed fruits and vegetables in Malawi. The effect of processing vegetables on phytochemicals was also evaluated.
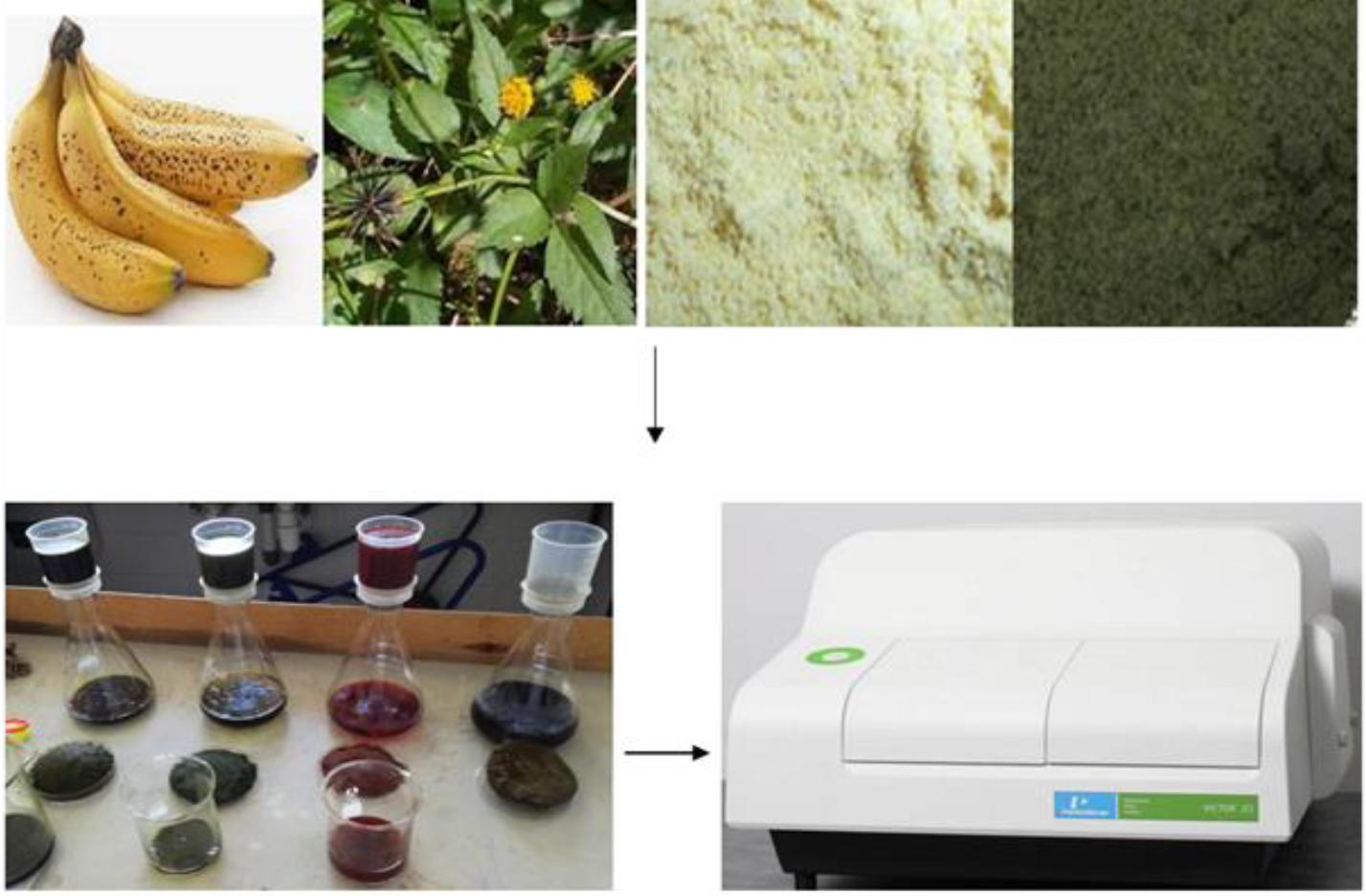
Methods: The potential of some commonly consumed fruits and vegetables in their raw and cooked forms as natural source of phytochemicals was evaluated in both aqueous and methanol extracts. These fruits and vegetables were screened for alkaloids, saponin, tannins, flavonoids, quinones, coumarins, terpenoids, steroids, glycosides and anthocyanins, total flavonoids content (TFC) and total phenol content (TPC) using standard procedures. TPC and TFC were also analyzed using spectrophotometric methods.
Results: Almost all the phytochemicals screened were found in some of the studied fruits and vegetables, with indigenous fruits and vegetables having the most, except for glycosides and anthocyanins. TPC in fruits ranged from 715.08mgGAE/g to 21,119.66mgGAE/g, while TFC ranged from 44.10mgQE/g to 434.74mgQE/g in vegetables. TPC of uncooked vegetables ranged from 522.22 mgGAE/g (pumpkin leaves) to 33, 684.66 mgGAE/g (ntoriro), while in cooked vegetables it ranged from 135.93 mgQE/g (bonongwe) to 6817.86 mgQE/g (chisoso). Overall, indigenous vegetables showed higher TPC values in comparison to exotic vegetables. It was also observed that processing of vegetables affected total phenolic compounds differently. In some vegetables, TPC values increased with cooking (pumpkin leaves, bonongwe and chisoso), while in others (cabbage, Chinese and rape) it decreased.
Conclusions: The results show that fruits and vegetables can serve as a cheap source of natural antioxidants that could help fight non-communicable diseases, such as hypertension, diabetes, and cancer. As might be expected, a single fruit or vegetable doesn’t contain all the necessary phytochemicals. Therefore, an intake of a mixture of fruits and vegetables is recommended for maximum benefit as functional foods.
Keywords: Phytochemicals, fruits, vegetables, total phenolic content, non-communicable diseases
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Any manuscripts or substantial parts of it, submitted to the journal must not be under consideration by or previously published in any other journal or citable form. Authors are required to ensure that no material submitted as part of a manuscript infringes existing copyrights or the rights of a third party. In submitting one's article in any form, the author has assigned the FFC publishing rights and has agreed to an automatic transfer of the copyright to the publisher. This is so that the FFC may create print option journals, for example, at the FFC’s discretion. If the author wishes to distribute their works by means outside of the FFC, for example within their community, they will have to place a request.
Correspondence concerning articles published in Functional Foods in Health and Disease is encouraged. While derivative works (adaptations, extensions on the current work, etc.) are allowed, distribution of the modified material is not allowed without permission from the FFC.